PREVENTING TECH NECK—How Can I Avoid It?
It’s not what you think!
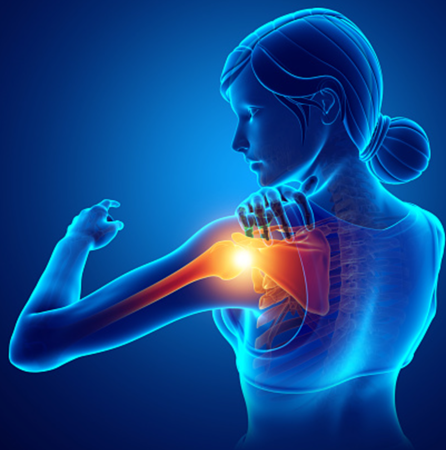
Tech neck is that posture we all assume when looking at our phones and devices. Studies show that we’re spending an average of 8-10 hours/day looking at those devices.
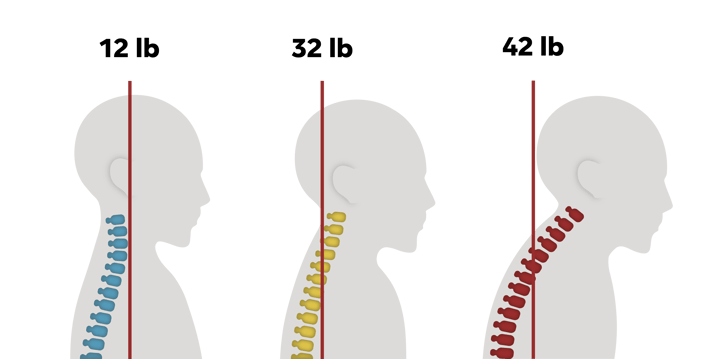
Did you know that your head can “weigh” up to 42lbs, depending how far forward it is held? Is there any question why we may be experiencing back and neck pain, tension, and headaches?
So, What Can I Do About It?
No one wants to end up looking like Quasimodo, but how do we avoid it? Since many of us spend most of our days sitting, we need to address sitting posture. Believe it or not, maintaining poor posture all day long creates muscle imbalances that then affect the way we stand. This is why it’s critical to sit well.
Contrary to what we’ve all been told, sitting is not the new smoking. We can learn to sit in a healthy way, which helps rather than hurts our bodies.
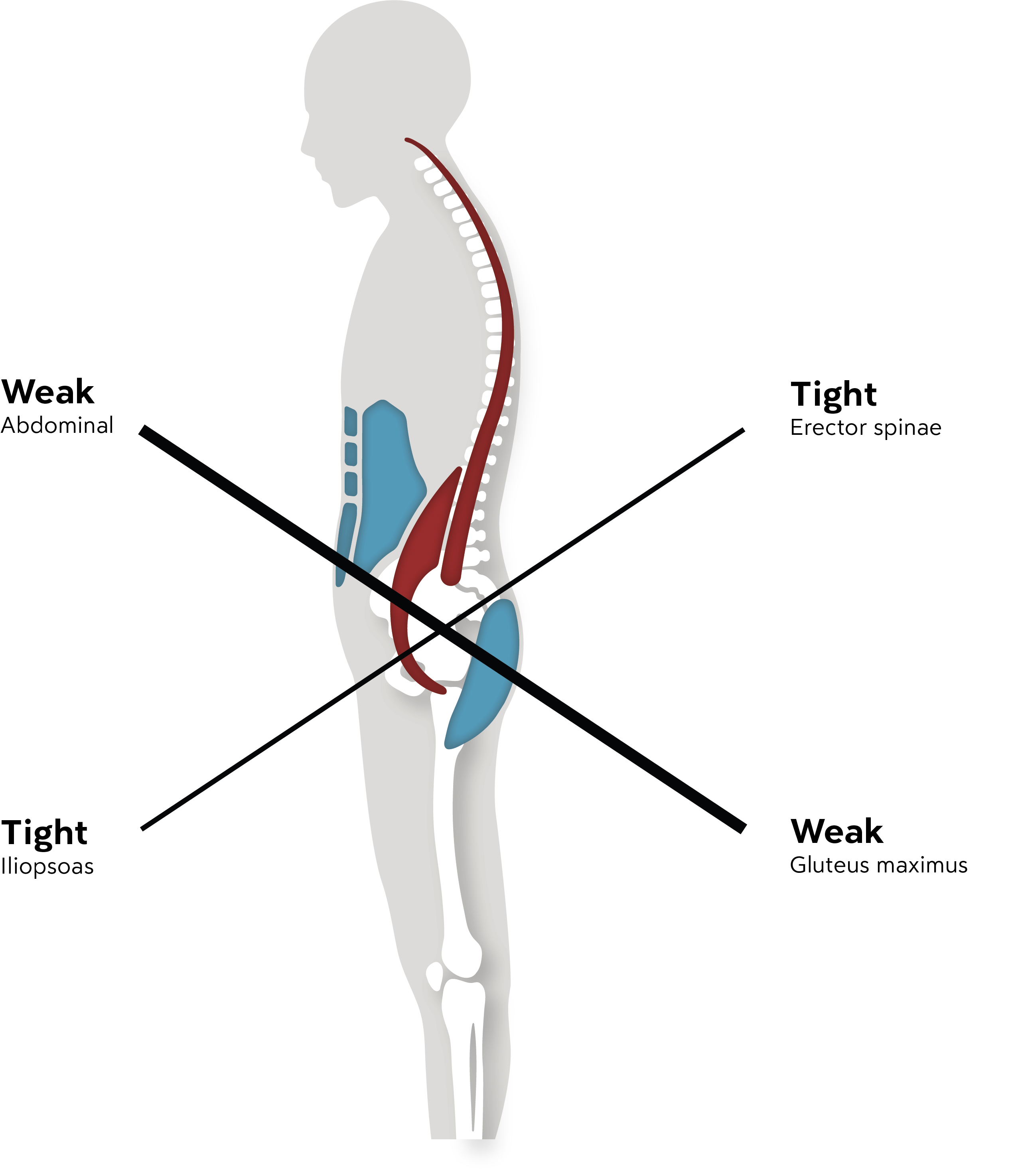
Remember the song Dem Bones, with the lyrics “the leg bone connected to the…thigh bone”? Well, the song is right—everything is connected, and neck posture begins with the position of the pelvis. Let’s review the anatomy of the spine and what are considered the “natural” curves of the spine. For the spine to remain in that upright position, with an “S” curve, the pelvis must be in a neutral position. The pelvis and spine are connected by ligaments, and because of this, any movement of the pelvis will affect the spine. We can imagine that the pelvis is the “foundation” of posture, and that foundation must be stabilized and supported.
That sounds easy, right?
The problem is that traditional office chairs don’t provide support to the pelvis specifically. Instead, they have incorporated “lumbar support,” which is typically a curve in the back support meant to meet the lumbar spine. There are two problems with this:
- Lumbar support is not adjustable. These curves won’t hit the “right” place on people of varying sizes and shapes!
- A lumbar support does not stabilize the pelvis, the foundation of the spine.
Traditional office chairs’ lack of pelvic support creates a slumped position and forward head posture.
Without the right support, over time the muscles in the lower back become fatigued, and the sitter will tend to relax them in favor of letting the ligaments help hold the torso upright. If postural support is not provided, the muscles of the lower back will tighten, and the person will slump down and forward. At the same time, the head will be pushed forward, forcing the muscles at the back of the neck to work to try to keep the head in the original position. Muscle tension at the cervical spine may increase as much as 50 percent when a person changes from an upright to a slumped posture (Semani, et al., 2012).1
The Solution
1You need an office chair that supports the body in the right places!
The ingredients of pain-free sitting as developed by medical professionals who specialize in sitting:
- Support your pelvis not lumbar
- Upper back relief
- Pressure-relieving contoured seat
- Tilt vs reclining resting position

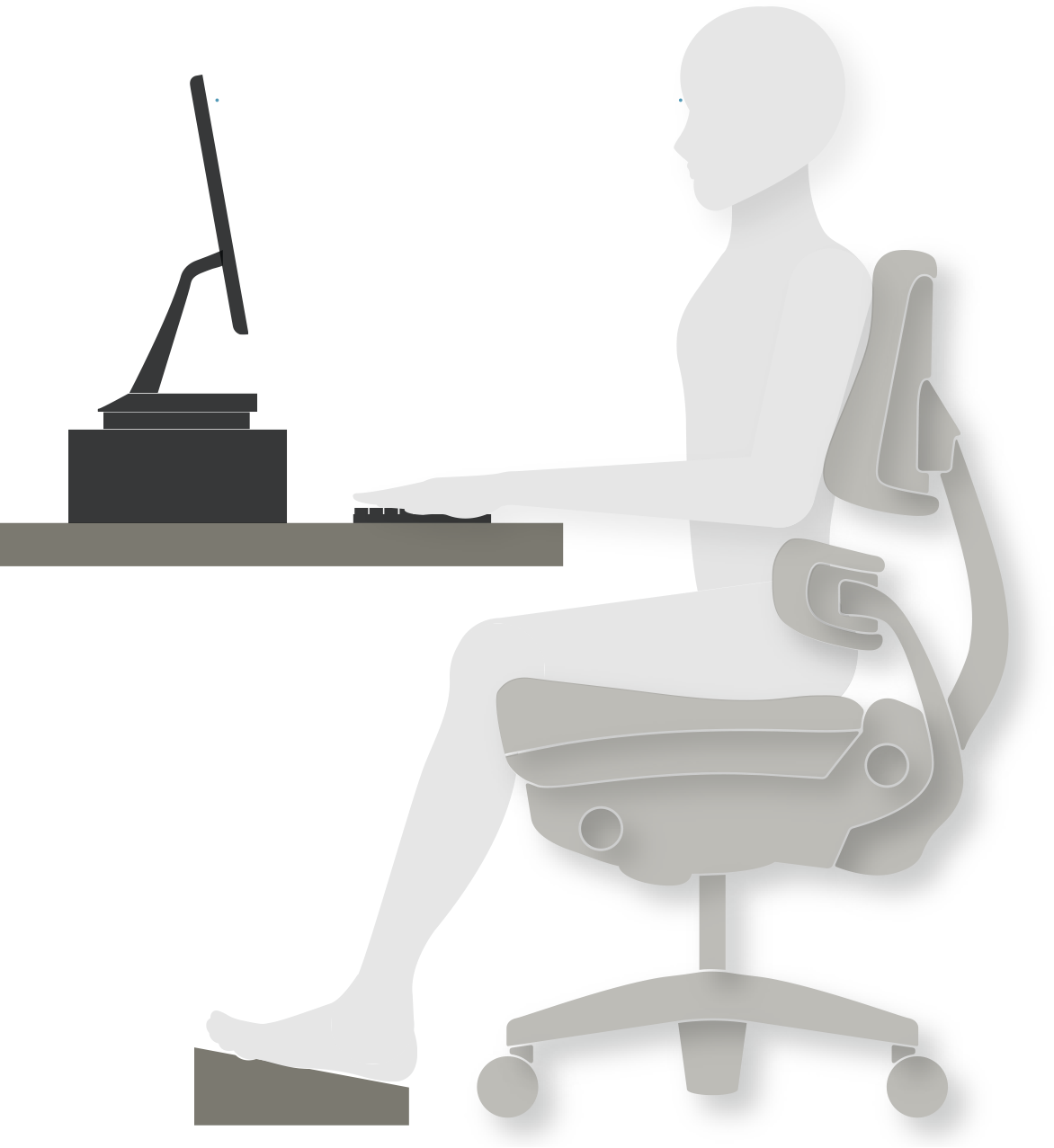
2 Set up your work space to optimize your work posture
3 Tech Neck Exercises
Performing exercises that promote muscle balance can help improve forward head posture.
1. Chin tucks- Stand with your upper back against a wall, feet shoulder-width apart.
- Face forward, tuck your chin down, and pull your head back until it meets the wall.
- Hold the stretch for 5 seconds before resting, and repeat 10 times.
- Place your left foot in front of you, bending your knee and placing your left hand on your left leg for stability.
- Place your right hand on your right hip to avoid bending at the waist. Keep your back straight and abdominal muscles tight.
- Tuck your pelvis, and you'll feel a stretch in your right thigh.
- Hold for 1min each side.
- Switch legs and repeat.
- Face a corner of a room or stand in a doorway. Place your forearms against each wall (or each door jamb) with your elbows slightly below shoulder level.
- Lean forward until you feel a stretch in your chest under your collarbone.
- Hold for up to a minute.
Reference:
- Mohammad Yadegaripour, Malihe Hadadnezhad, Ali Abbasi, Fereshteh Eftekhari & Afshin Samani (2021) The Effect of Adjusting Screen Height and Keyboard Placement on Neck and Back Discomfort, Posture, and Muscle Activities during Laptop Work, International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction, 37:5, 459-469, DOI: 10.1080/10447318.2020.1825204
Recent Post

Anthros Decompress Mode: A New Way to Sit, Move, and Recover
December 23, 2025Adding a cushion to your office or gaming chair...

Four Lessons About Seating Everyone Can Learn from Wheelchair Users
September 18, 2025Working with wheelchair users has been an...